Arithmetic Mean [ Individual Series] Direct Method and Short-cut Method
Measures of Central
Tendency or Averages
Measures of central tendency
refers to all those methods of statistical analysis which are used to calculate
the average of a set of data.
According to Clark and Sekkade, “Average
is an attempt to find one single figure to describes whole of figures”.
Types of averages-
1-
Mathematical
averages: The mathematical averages are Arithmetic mean, Geometric mean and Harmonic
mean.
2-
Positional averages:
The positional averages are Median and Mode.
Arithmetic mean
Arithmetic mean or arithmetic
average is defined as the sum of all values divided by the number of values.
There are two types of Arithmetic
mean:
1-Simple Arithmetic mean
2-Weighted Arithmetic mean
Simple Arithmetic mean- Individual series
Direct Method- The simple arithmetic mean of a series is equal to the sum of variables
divided by their number.
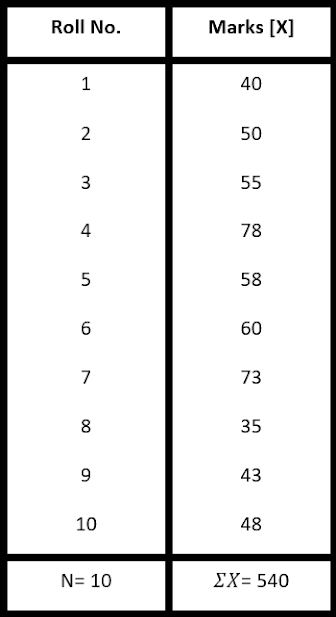
Question 1[a]- Calculate the
arithmetic mean from the following data by using direct method:
Roll No- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Marks: 40, 50, 55, 78, 58, 60, 73, 35, 43, 48
Short cut method- The arithmetic mean can also be calculated by short cut method. This method reduces the amount of calculation. It involves the following steps:
1- Assume any one value as an assumed mean which is also known as working mean or arbitrary average [A].
2- Find out the difference of each value [deviation] from the assumed mean [d = X-A].
3- Add all the deviation [Σd].
4- Apply the formula
Question 2[a]- Calculate the arithmetic
mean of the following data of marks of a group of students by using direct
method:
Students- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Marks: 10, 15, 18, 20, 22, 25, 30, 35, 25, 17
Question 2[b]- Calculate the arithmetic mean from the
following data by using short cut method.
Students: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Marks: 10, 15, 18, 20, 22, 25, 30, 35, 25, 17
Question 3[a]- Calculate the arithmetic
mean of the following data of marks of a group of students by using direct
method:
Students- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Marks [X]- 25,
30, 21, 55, 47, 10, 15, 17, 45, 35
Question 3[b]- Calculate the arithmetic mean from the following data by using short cut method.
Students- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Marks [X]- 25,
30, 21, 55, 47, 10, 15, 17, 45, 35
Question 4[a]- Calculate the arithmetic mean from the following data by using direct method.
Month: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun
Income (Rs): 25000, 30000, 45000, 20000, 25000, 20000
Question 4[b]- Calculate the arithmetic mean from the following data by using short cut method.
Month: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun
Income (Rs): 25000, 30000, 45000, 20000, 25000, 20000
Question 5[a]-Calculate the arithmetic mean from the following data
by using direct method.
Families- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Daily Income in Rs. [X]- 18, 20, 35, 55, 38, 54, 100, 85, 37, 53
Question 5[b]-Calculate mean from
the following data by using short cut method.
Families- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Daily Income in Rs. [X]- 18, 20, 35,
55, 38, 54, 100, 85, 37, 53









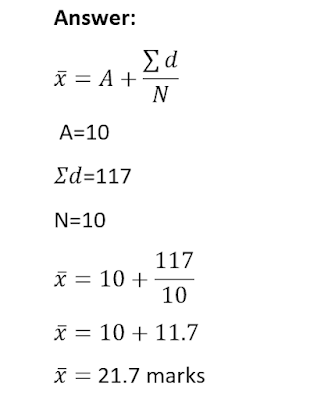















Thanks a lot Mam for providing your notes.
ReplyDelete